Exploring the Epidemiology and Research Advances of Endemic Syphilis or Bejel
 |
| Bejel: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention, Healthnews // News Medical |
Bejel Found in Arid Regions of the World
Healthnews: Bejel, also known as endemic syphilis, is a chronic bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum subsp. endemicum. It is primarily found in arid regions of the world, such as the Middle East, North Africa, and Central Australia, and is transmitted through close contact with infected individuals.
Bejel is primarily found in arid regions of the world, including the Middle East, North Africa, and Central Australia, where it is transmitted through close contact with infected individuals.
The symptoms of bejel can be similar to those of other sexually transmitted infections and skin conditions, making diagnosis challenging. Blood tests and examination of affected tissue are typically used to diagnose the infection.
Penicillin is the preferred antibiotic for treating bejel, and a single injection can cure the infection if administered early. Close follow-up with a healthcare provider is necessary to monitor the response to treatment and ensure successful resolution of the infection.
Individuals with bejel may remain at risk for reinfection if they continue to engage in behaviors that increase their risk of exposure to the bacterium. Therefore, prevention efforts, such as practicing safe sex and reducing the risk of sexually transmitted infections, are essential for controlling the spread of the disease.
Research on bejel has helped to improve our understanding of the disease and inform effective prevention and treatment strategies. However, more research is needed to address remaining gaps in our knowledge of this condition, particularly with regard to its long-term effects on affected individuals.
 |
| Bejel: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention, Healthnews // Cleveland Clinic |
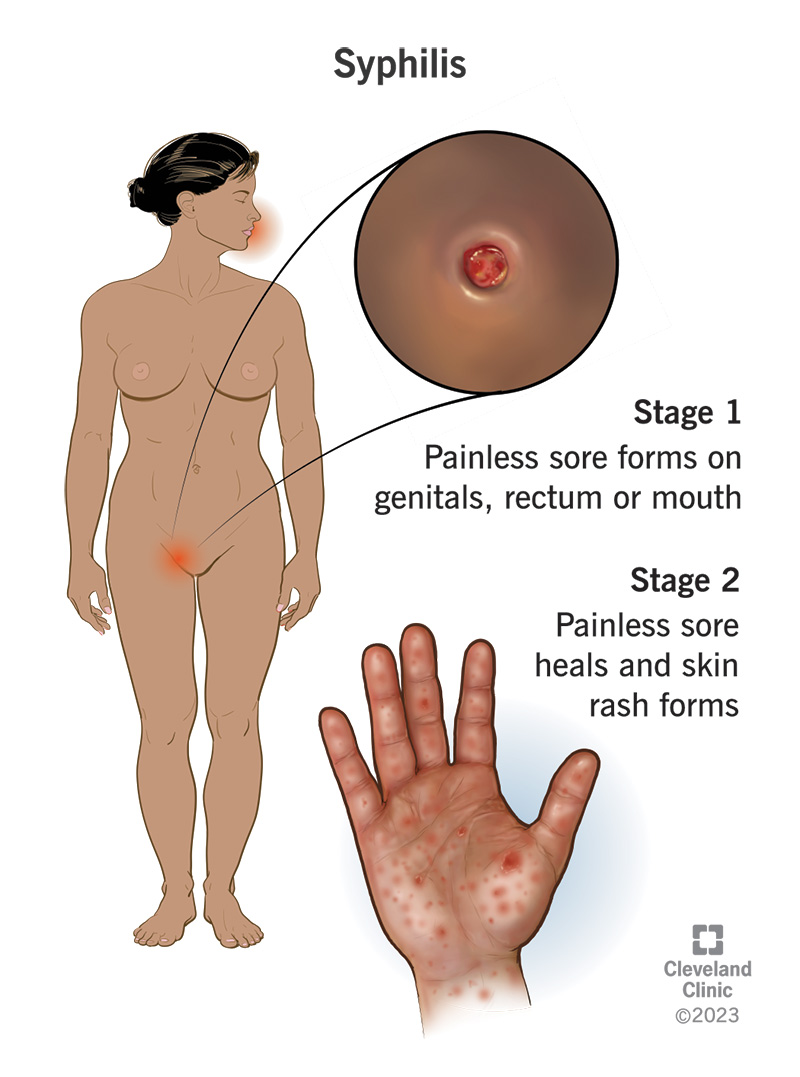
The symptoms of bejel, also known as endemic syphilis, can vary depending on the stage of the infection. The disease has four stages: primary, secondary, latent, and late.
Primary stage:
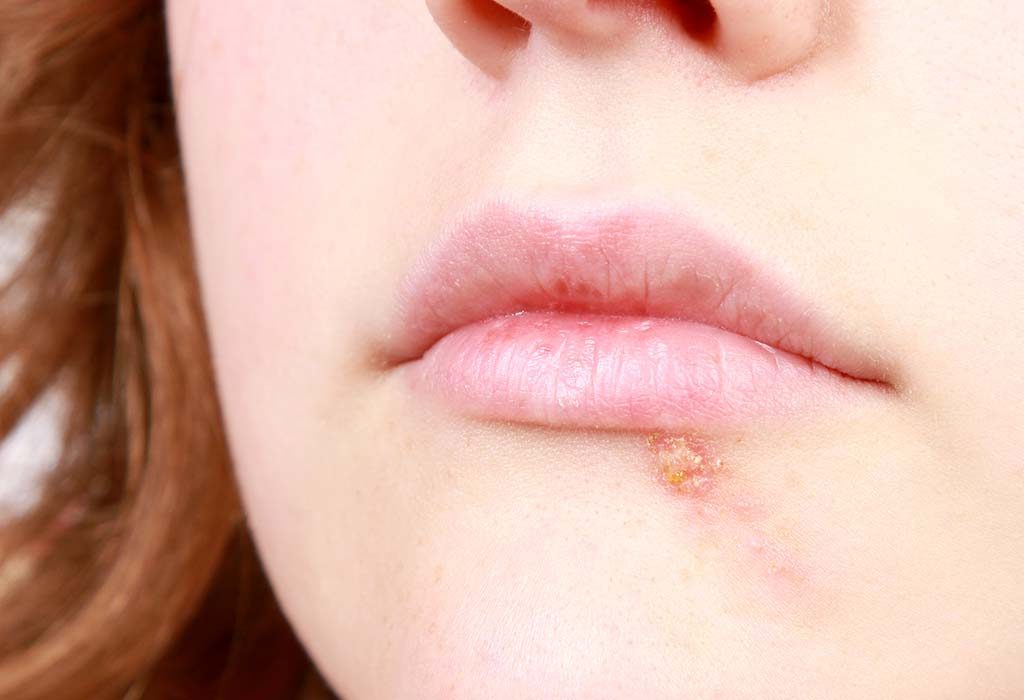
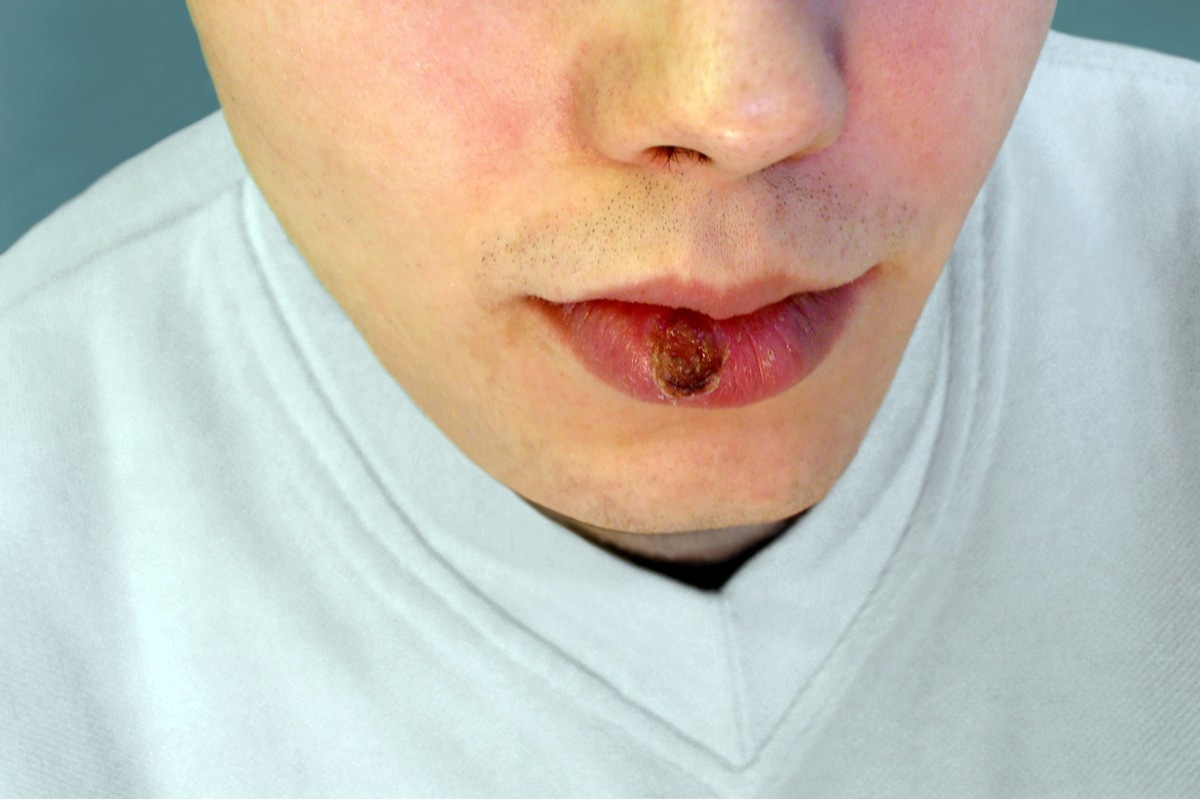
- A painless, red, firm, and round sore called a chancre appears on the skin, typically on the genitals, anus, or mouth, where the bacterium enters the body.
- The sore can persist for several weeks before it goes away, but the bacteria continue to multiply and spread throughout the body.
Secondary stage:
- A rash, which may be red or brown, develops on the trunk and extremities, including the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
- Lesions may also appear in the mouth, throat, and genitals.
- Other symptoms may include fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue.
Latent stage:
- The infection becomes asymptomatic and may last for years.
- Although there are no symptoms, the bacterium can still be present in the body and can cause complications in later stages.
Late stage:
- If left untreated, bejel can progress to late-stage complications, which can affect multiple organ systems.
- These complications may include destructive lesions of the bones and joints, chronic ulcers, and cardiovascular disease.
It is important to note that the symptoms of bejel can be similar to those of other sexually transmitted infections and skin conditions, so it is essential to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The treatment for bejel, also known as endemic syphilis, involves a course of antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection. The choice of antibiotic and duration of treatment depend on the stage of the disease and the individual's medical history.
In general, penicillin is the preferred antibiotic for treating bejel. Depending on the stage of the disease and individual factors, other antibiotics, such as doxycycline or azithromycin, may also be used.
The duration of antibiotic treatment may vary depending on the stage of the infection. For early-stage bejel, a single injection of penicillin is usually sufficient to cure the infection. For later stages, a longer course of antibiotics may be necessary, and close follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential to monitor the response to treatment.
It is important to note that even after successful treatment, individuals with bejel may remain at risk for reinfection if they continue to engage in behaviors that increase their risk of exposure to the bacterium. Therefore, it is essential to practice safe sex and take other measures to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections.
 |
| Bejel: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention, Healthnews // Medicover Hospital |
Prevention is Key to Stopping the Spread of Bejel
Prevention of bejel involves measures to reduce the risk of exposure to the bacterium that causes the infection. Some key strategies for preventing bejel include:
- Practicing safe sex: Bejel is primarily transmitted through close contact with infected individuals, including sexual contact. Therefore, using barrier methods such as condoms during sexual activity can reduce the risk of transmission.
- Getting tested and treated: Early detection and treatment of bejel can help prevent the spread of the infection. It is important to get tested for sexually transmitted infections regularly, particularly if engaging in high-risk behaviors.
- Educating and raising awareness: Raising awareness about bejel and other sexually transmitted infections can help to reduce stigma and increase understanding of the importance of prevention and treatment.
- Improving hygiene and sanitation: Bejel is more common in areas with poor hygiene and sanitation, so improving living conditions and access to clean water can help reduce the risk of transmission.
- Addressing social and economic factors: Bejel is more common among marginalized populations, including those living in poverty or experiencing conflict or displacement. Addressing social and economic factors that contribute to these disparities can help to reduce the burden of bejel and other sexually transmitted infections.
By taking these preventive measures, we can help reduce the risk of bejel and other sexually transmitted infections and promote overall health and well-being.
.png)