What is Chronic Sinusitis
 |
| Dealing with Chronic Sinusitis: Causes and Treatments, Healthnews // ENT |
Clearing the Air Understanding Chronic Sinusitis
What is Chronic Sinusitis
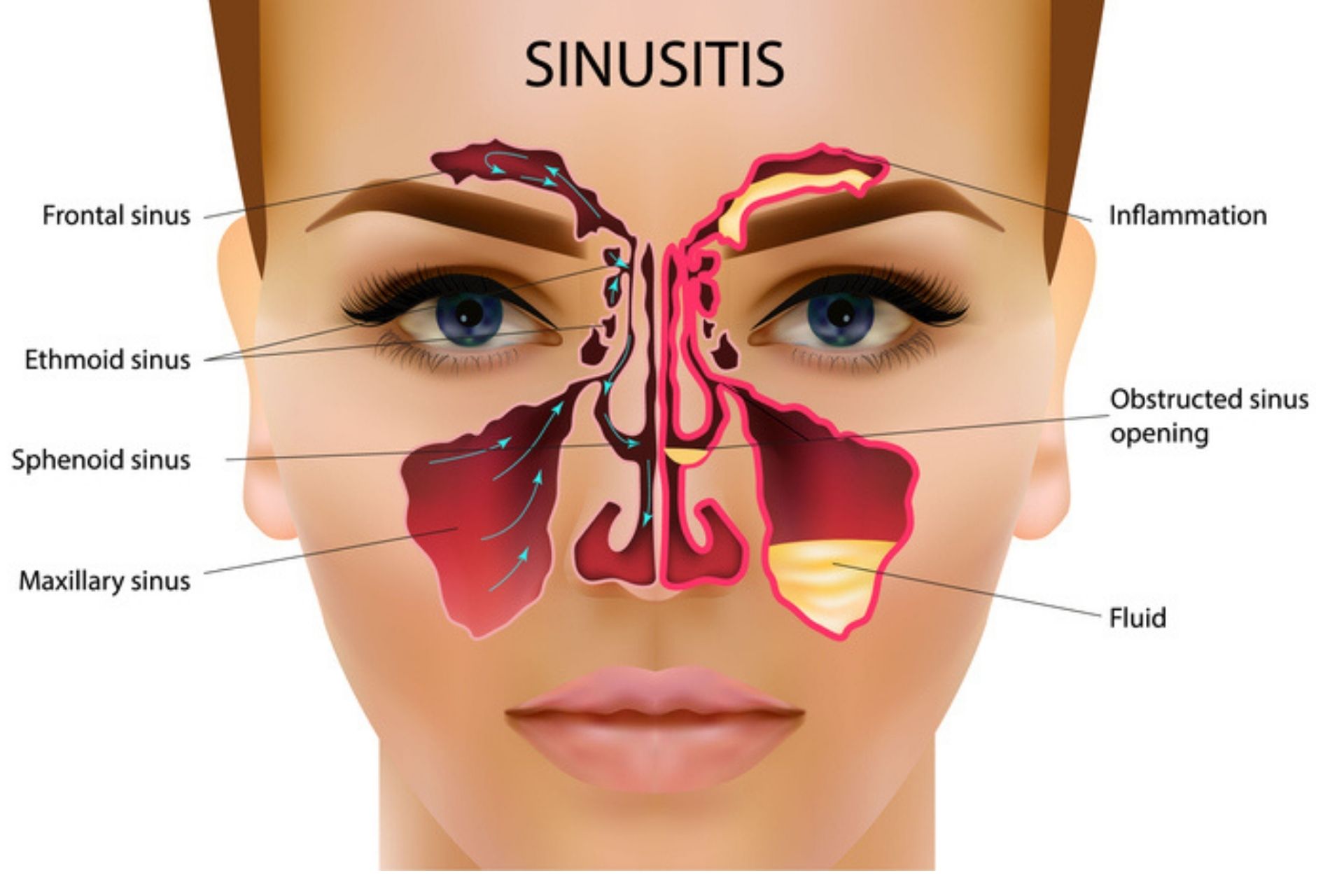
HealthNews: Chronic sinusitis is a long-term inflammation of the sinuses, which are air-filled spaces located in the bones of the face and skull. It is typically characterized by symptoms such as facial pain and pressure, nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, and a reduced sense of smell and taste. Chronic sinusitis can significantly impact a person's quality of life and may require medical intervention to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
According to research
According to research, chronic sinusitis affects approximately 11% of the adult population in the United States. It is more prevalent in women and individuals with allergies or asthma. The condition can be caused by various factors, including bacterial or fungal infections, structural abnormalities in the sinuses, and immune system disorders. Diagnosis of chronic sinusitis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests, such as CT scans. Treatment options may include antibiotics, nasal corticosteroids, saline nasal irrigation, and surgery in severe cases. Effective management of chronic sinusitis can improve symptoms and prevent complications such as recurring infections, nasal polyps, and sinusitis-related headaches.
Causes chronic sinusitis
Chronic sinusitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can cause chronic sinusitis. These infections can lead to inflammation of the sinuses and produce symptoms that persist for several weeks or more.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to environmental factors such as pollen, dust mites, and animal dander can cause chronic inflammation of the sinuses.
- Structural abnormalities: Structural problems in the nasal cavity or sinuses, such as a deviated septum or nasal polyps, can lead to chronic sinusitis by obstructing the sinuses and preventing proper drainage.
- Immune system disorders: Certain immune system disorders, such as cystic fibrosis or immunodeficiency disorders, can increase the risk of developing chronic sinusitis.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to pollutants, cigarette smoke, and other environmental irritants can also cause chronic sinusitis by inflaming the sinuses and causing congestion.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): GERD, a digestive disorder in which stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, can cause irritation and inflammation of the sinuses.
- Dental infections: Infections in the teeth or gums can spread to the sinuses and cause chronic sinusitis.
- Medications: Long-term use of certain medications such as nasal decongestant sprays, aspirin, and ibuprofen can cause chronic sinusitis by irritating the lining of the sinuses.
- Genetic predisposition: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to developing chronic sinusitis.
- Other medical conditions: Chronic sinusitis can be associated with other medical conditions such as asthma, nasal septum deviation, and inflammatory bowel disease.
It's essential to identify the underlying cause of chronic sinusitis to determine the most effective treatment options. A healthcare provider may conduct a physical examination, review the medical history of the patient, and perform imaging tests to diagnose the condition and rule out other potential causes.
 |
| Chronic Sinusitis: Causes and Treatments, Healthnews // iStock |
Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Options for Chronic Sinusitis Sufferers
- Stage 4 Lung Cancer to Look Out For
- Cough Cures Unveiled 12 Natural Remedies and Medicine Ingredients
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- Prioritize Your Health Tips and Tricks for Well-being
Chronic Sinusitis Symptoms
The symptoms of chronic sinusitis can vary from person to person, but typically include:
- Nasal congestion: This is often the most common symptom of chronic sinusitis. It can be severe and persistent, making it difficult to breathe through the nose.
- Facial pain and pressure: Pain and pressure are often felt in the forehead, between the eyes, and in the cheeks and upper teeth.
- Reduced sense of smell and taste: Chronic sinusitis can cause a reduced sense of smell and taste due to inflammation and congestion in the nasal passages.
- Discolored nasal discharge: Thick, discolored mucus may drain from the nose or down the back of the throat.
- Headaches: Headaches are common with chronic sinusitis and are often due to the pressure and inflammation in the sinuses.
- Fatigue: Chronic sinusitis can cause fatigue and malaise, particularly if it disrupts sleep.
- Coughing: A persistent cough may occur due to postnasal drip, which is the mucus that drips down the back of the throat from the sinuses.
- Sore throat: Sore throat can occur due to the drainage of mucus from the sinuses down the back of the throat.
- Ear pain: Ear pain can occur due to the pressure from inflamed sinuses on the Eustachian tubes that connect the nose and ear.
These symptoms can persist for more than 12 weeks and can significantly affect a person's quality of life. If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to seek medical advice from a healthcare provider.
 |
| Chronic sinusitis is a condition that affects many people worldwide, Healthnews // Ayurveda treatment |
The treatment of chronic sinusitis depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Some treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: If the cause of chronic sinusitis is a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to clear the infection.
- Nasal corticosteroids: These medications are commonly used to reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and sinuses, allowing for better drainage and relief of symptoms.
- Saline nasal irrigation: This involves flushing the nasal passages with a saline solution to help remove mucus and improve sinus drainage.
- Decongestants: These medications can be used to relieve nasal congestion, but should only be used for a short period, as they can have side effects such as high blood pressure and increased heart rate.
- Immunotherapy: If the underlying cause of chronic sinusitis is allergies, immunotherapy may be recommended to help reduce the body's sensitivity to allergens.
- Surgery: In cases where chronic sinusitis is caused by structural abnormalities, such as nasal polyps or a deviated septum, surgery may be necessary to correct the issue.
- Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and reducing exposure to environmental irritants, can help reduce symptoms of chronic sinusitis.
Chronic sinusitis can be a complex condition, and treatment may require a combination of different approaches. A healthcare provider can help determine the best course of action based on the individual's specific symptoms and underlying causes.
Conclusion is
Chronic sinusitis is a condition that affects many people worldwide and can significantly impact their quality of life. It is caused by inflammation and swelling of the sinuses, leading to symptoms such as nasal congestion, facial pain and pressure, reduced sense of smell and taste, and headaches, among others. While the underlying causes of chronic sinusitis can be complex and varied, there are effective treatment options available, including antibiotics, nasal corticosteroids, saline nasal irrigation, immunotherapy, and surgery, among others. Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and reducing exposure to environmental irritants can also help reduce symptoms. If you are experiencing symptoms of chronic sinusitis, it is important to seek medical advice from a healthcare provider who can diagnose the condition and recommend an appropriate course of treatment.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pescatarian-diet-4174528-a-08ad1e53f16845d2bf69d36ff65257f0.jpg)