Herpes Simplex Virus Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Herpes Simplex Virus Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
What is Herpes simplex virus
Health News: Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a highly contagious virus that belongs to the family of herpesviruses. There are two types of herpes simplex virus: HSV-1 and HSV-2.
HSV-1 typically causes oral herpes, which presents as cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth and on the lips. HSV-2, on the other hand, usually causes genital herpes, which presents as sores or blisters around the genital area.
HSV-1
HSV-1 (Herpes simplex virus type 1) is a highly contagious virus that primarily causes oral herpes or cold sores around the mouth and on the lips. It is transmitted through direct contact with an infected person's saliva, such as kissing or sharing utensils. Once a person is infected, the virus can remain dormant in the body's nerve cells and reactivate, causing recurrent outbreaks of cold sores.
HSV-1 can also cause genital herpes through oral-genital contact, although this is less common than genital herpes caused by HSV-2. While there is no cure for HSV-1, antiviral medications can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. It is important to practice good hygiene and avoid close contact with others during outbreaks to reduce the risk of spreading the virus.
HSV-2
HSV-2 (Herpes simplex virus type 2) is a highly contagious virus that primarily causes genital herpes, which presents as painful sores or blisters around the genital area. HSV-2 is transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
Once a person is infected, the virus can remain dormant in the body's nerve cells and reactivate, causing recurrent outbreaks of genital herpes. While there is no cure for HSV-2, antiviral medications can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. It is important to practice safe sex, including the use of condoms, to reduce the risk of contracting or spreading HSV-2.
Both types of herpes simplex virus can be spread through direct contact with an infected person, including sexual contact, kissing, and sharing personal items such as towels or razors. Once a person is infected with the herpes simplex virus, the virus remains in the body and can cause outbreaks of sores or blisters throughout a person's lifetime. While there is no cure for herpes simplex virus, antiviral medications can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
 |
| Herpes Simplex Virus, Healthnews // Planning |
According to Research
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) has been extensively researched over the years, and there is a vast body of scientific literature on the topic. Some of the key findings from this research include:
- HSV is a highly prevalent virus: It is estimated that up to 90% of adults have been exposed to HSV-1, while around 16% of adults have been exposed to HSV-2.
- HSV can be transmitted even when there are no symptoms: People with herpes can shed the virus even when they have no visible symptoms, which can make it challenging to prevent transmission.
- Antiviral medications can help manage the symptoms: While there is no cure for HSV, antiviral medications can help reduce the severity and frequency of outbreaks. In some cases, daily suppressive therapy can help prevent outbreaks altogether.
- HSV can have significant psychological and social impacts: Herpes can be a source of significant stress and stigma for those who are infected, which can lead to depression, anxiety, and other psychological problems.
- Prevention strategies are important: Practicing safe sex, using condoms, and avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks can all help reduce the risk of contracting or spreading HSV.
The research on HSV underscores the importance of effective prevention and management strategies for this common virus.
R E A D :
- Conquering Vaginal Bacterial Infections Causes, Complications, and Prevention Tips
- HIV-AIDS Unveiled Understanding the Virus
- Melanoma Unpacked Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options Explained
- The Silent Agony: Unveiling the Mystery of Ménière's Diseas
- Understanding Leukemia Causes Symptoms and Treatment Options
Herpes Simplex Virus Transmission Understanding the Causes and Prevention
The causes
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is caused by the herpes simplex virus. There are two types of herpes simplex virus: HSV-1 and HSV-2.
HSV-1 is typically transmitted through direct contact with an infected person's saliva, such as kissing or sharing utensils. It can also be spread through oral-genital contact, although this is less common.
HSV-2 is primarily transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
Once a person is infected with the herpes simplex virus, the virus can remain dormant in the body's nerve cells and reactivate, causing recurrent outbreaks of sores or blisters. Outbreaks can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, illness, hormonal changes, and exposure to sunlight.
To note that herpes simplex virus can be transmitted even when there are no visible symptoms, which can make it challenging to prevent transmission. Practicing safe sex, using condoms, and avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks can all help reduce the risk of contracting or spreading HSV.
The symptoms
The symptoms of Herpes simplex virus (HSV) can vary depending on the type of virus and the location of the infection. Here are some common symptoms:
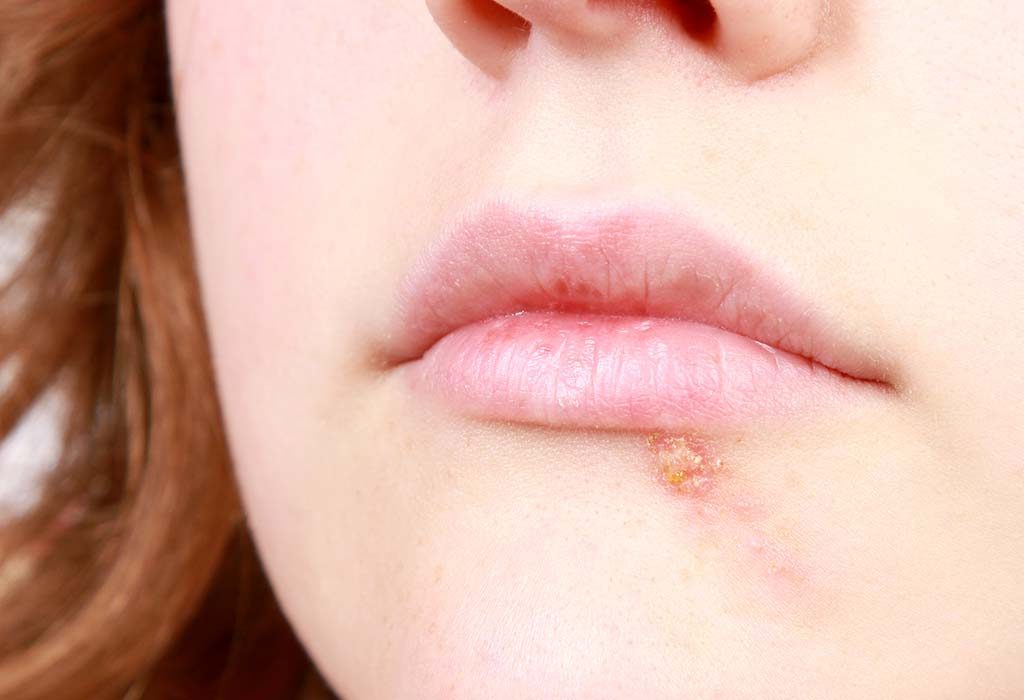
- Oral herpes (HSV-1): Typically presents as cold sores or blisters around the mouth or on the lips. These sores can be painful, and may be accompanied by fever, swollen lymph nodes, and other flu-like symptoms.
- Genital herpes (HSV-2): Presents as painful sores or blisters around the genital area, anus, or buttocks. These sores can be accompanied by itching, burning, and other symptoms. Some people may also experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever and swollen glands.
In both types of herpes, the first outbreak is usually the most severe. Subsequent outbreaks tend to be milder and less frequent over time. However, the virus remains in the body and can reactivate, causing recurrent outbreaks throughout a person's lifetime.
It is important to note that some people with herpes may not experience any visible symptoms. This is known as asymptomatic herpes, and it can still be transmitted to others. If you suspect that you may have herpes, it is important to get tested and talk to a healthcare provider about treatment and prevention options.
 |
| Herpes Simplex Virus, Healthnews // Dreamstimes |
Treatment method
There is no cure for Herpes simplex virus (HSV), but antiviral medications can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. Here are some common treatment methods:
- Antiviral medications: Drugs like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir can help reduce the duration and severity of outbreaks. They work by inhibiting the replication of the virus and can be taken episodically or as daily suppressive therapy.
- Topical medications: Creams and ointments like docosanol and lidocaine can help relieve pain and discomfort associated with herpes outbreaks.
- Pain relief medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and aspirin can help reduce pain and fever associated with herpes outbreaks.
- Good hygiene: Keeping the affected area clean and dry can help prevent the spread of the virus and reduce the risk of secondary infections.
- Lifestyle changes: Managing stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding triggers like excessive sun exposure and alcohol consumption can help reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
It is important to talk to a healthcare provider about the best treatment options for your individual situation. Additionally, practicing safe sex, using condoms, and avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks can all help reduce the risk of contracting or spreading HSV.
* Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a highly prevalent virus that can cause oral or genital herpes. The virus can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person's saliva or through sexual contact. Once a person is infected, the virus can remain dormant in the body and reactivate, causing recurrent outbreaks of painful sores or blisters. While there is no cure for HSV, antiviral medications and other treatments can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. Practicing safe sex, using condoms, and avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks can also help reduce the risk of contracting or spreading HSV. If you suspect that you may have herpes, it is important to talk to a healthcare provider about testing and treatment options.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-fruitarian-diet-4682619-a-dd163e61ab234f6b9f5149dc49fa1ac6.jpg)