Understanding Bacterial Meningitis and How to Stay Safe
 |
| Silent Killer Bacterial Meningitis Awareness and Prevention, Health news // Passport health |
Don't Let Bacterial Meningitis Catch You Off Guard: Know the Symptoms and Protect Yourself Now
Bacterial meningitis?
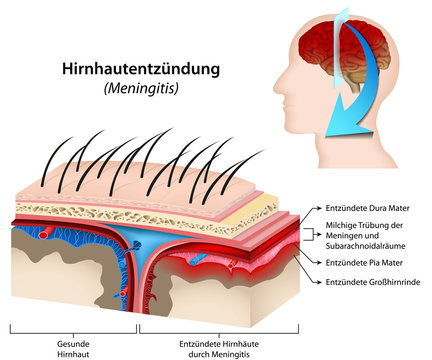
>> Bacterial meningitis is a serious infection that affects the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, or Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), which can invade the bloodstream and travel to the brain and spinal cord, causing inflammation and swelling of the meninges.
Bacterial meningitis can cause symptoms such as fever, headache, stiff neck, sensitivity to light, nausea, vomiting, confusion, and seizures. It is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment with antibiotics and sometimes other supportive therapies such as oxygen or IV fluids. Without treatment, bacterial meningitis can lead to brain damage, hearing loss, and even death.
Prevention of bacterial meningitis includes vaccination against the bacteria that can cause it, practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with sick people, and seeking prompt medical attention if symptoms appear.
ACCORDING TO RESEARCH Bacterial meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is a well-researched topic in the medical field, and there have been many studies conducted on this condition. Research has shown that the incidence of bacterial meningitis varies depending on geographic location, age, and underlying health conditions. Infants, young children, and the elderly are at higher risk of developing bacterial meningitis.
Diagnosis of bacterial meningitis usually involves a physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies such as CT scans or MRI, and a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) to collect cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
Prompt treatment with antibiotics is critical in improving outcomes for bacterial meningitis patients. In addition, research has shown that early identification and treatment of close contacts of a person with meningitis can help prevent the spread of the disease.
Vaccination is also an important prevention strategy for bacterial meningitis. Vaccines are available for the bacteria that commonly cause meningitis, including Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib).
 |
| Understanding Bacterial Meningitis and How to Stay Safe, Health news // Adobe stock |
Bacterial meningitis is caused by certain types of bacteria that invade the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, known as the meninges. The most common bacterial causes of meningitis include:
Neisseria meningitidis: This bacteria is spread through respiratory and throat secretions and can cause meningococcal meningitis, which is a leading cause of bacterial meningitis in children and young adults.
Streptococcus pneumoniae: This bacteria is a common cause of bacterial meningitis in young children and older adults. It can also cause pneumonia and other infections.
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib): Before the widespread use of the Hib vaccine, this bacteria was a common cause of meningitis in young children.
Other less common causes of bacterial meningitis include Listeria monocytogenes and Group B Streptococcus.
The bacteria that cause meningitis can spread through close contact with an infected person, such as through coughing, sneezing, or kissing. People who have weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk of developing bacterial meningitis. It is important to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect you or someone else may have bacterial meningitis, as early treatment is crucial in improving outcomes.
R E A D :
- What You Need to Know About Dementia Types, Risk Factors, and How to Recognize Symptoms
- Unraveling the Mystery of Excessive Mucus: 8 Potential Causes You Should Know About
- Unlock Vitality: 10 Common Habits that Drain Energy Levels Unknowingly
What symptoms
Bacterial meningitis can cause a range of symptoms that can develop suddenly and progress rapidly. The symptoms of bacterial meningitis can vary depending on the age of the person affected, but some common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Stiff neck
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Confusion and irritability
- Drowsiness and difficulty waking up
- Seizures
- Skin rash (in some cases)
- In infants, bacterial meningitis symptoms can include:
- High-pitched crying or moaning
- Refusing to eat or drink
- Bulging fontanelle (the soft spot on the top of the head)
- Excessive sleepiness or difficulty waking up
 |
| Silent Killer Bacterial Meningitis Awareness and Prevention, Health news // Twitter |
Method of treatment
The treatment for bacterial meningitis typically involves hospitalization and administration of antibiotics as soon as possible. Antibiotics are given intravenously (IV) to ensure that they reach the cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, which is where the bacteria causing the infection is located.
The choice of antibiotics depends on the type of bacteria that is causing the meningitis, as well as the age and overall health of the patient. The antibiotics are usually given for a period of 7 to 21 days, depending on the severity of the infection.
In addition to antibiotics, patients with bacterial meningitis may require supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications. This can include:
- Pain relief medication for headaches and body aches
- Anti-seizure medication to prevent seizures
- Oxygen therapy to maintain adequate oxygen levels in the blood
- Intravenous fluids to maintain hydration
- Steroids to reduce inflammation and swelling of the brain and spinal cord
Patients with severe bacterial meningitis may require intensive care and monitoring, and some may need mechanical ventilation to assist with breathing.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for improving outcomes for patients with bacterial meningitis. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know has symptoms of meningitis, as the condition can be life-threatening if left untreated.
>> Bacterial meningitis is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that is caused by certain types of bacteria that invade the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. The symptoms of bacterial meningitis can include fever, headache, stiff neck, nausea and vomiting, sensitivity to light, confusion, drowsiness, seizures, and skin rash.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are crucial for improving outcomes for patients with bacterial meningitis. In addition to antibiotics, patients with bacterial meningitis may require supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
R E A D : Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: Understanding a Rare Genetic Disorder and its Dental Manifestations
Prevention strategies for bacterial meningitis include vaccination, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and covering coughs and sneezes.
If you suspect that you or someone you know may have bacterial meningitis, it is important to seek medical attention immediately, as early treatment can greatly improve outcomes for this potentially life-threatening condition.

ليست هناك تعليقات:
إرسال تعليق