Advancements in Leukemia Treatment New Hope for Patients
Exploring the Latest Developments in Chemotherapy, Immunotherapy, and Targeted Therapy for Leukemia
R E A D : The Connection Between Diet and Sleep: How What You Eat Affects Your Rest
WHAT IS Leukemia ?
Healthnews: Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, which are responsible for producing blood cells. It is a cancer of the white blood cells, which are cells that are involved in fighting infections in the body.
Leukemia is characterized by the abnormal growth and proliferation of white blood cells in the bone marrow. These cells can interfere with the production of normal blood cells, which can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications.
There are several different types of leukemia, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Each type of leukemia is characterized by different types of abnormal cells and can have different symptoms and treatment options.
Leukemia is typically treated with a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and bone marrow transplantation, depending on the type and stage of the cancer. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many people with leukemia are able to achieve long-term remission and live healthy, productive lives.
* causes and symptoms of Leukemia Cancer
The exact causes of leukemia are not fully understood, but there are several risk factors that have been identified, including:
> Genetic factors: Some genetic mutations may increase the risk of developing leukemia.
R E A D : Uncovering the Signs: 10 Less Recognized Symptoms of Unhealthy Lungs You Must Not Disregard
> Environmental factors: Exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, and other environmental factors may increase the risk of developing leukemia.
> Previous cancer treatment: Previous treatment with chemotherapy and radiation therapy for other types of cancer may increase the risk of developing leukemia.
> Age: Leukemia is more common in older adults.
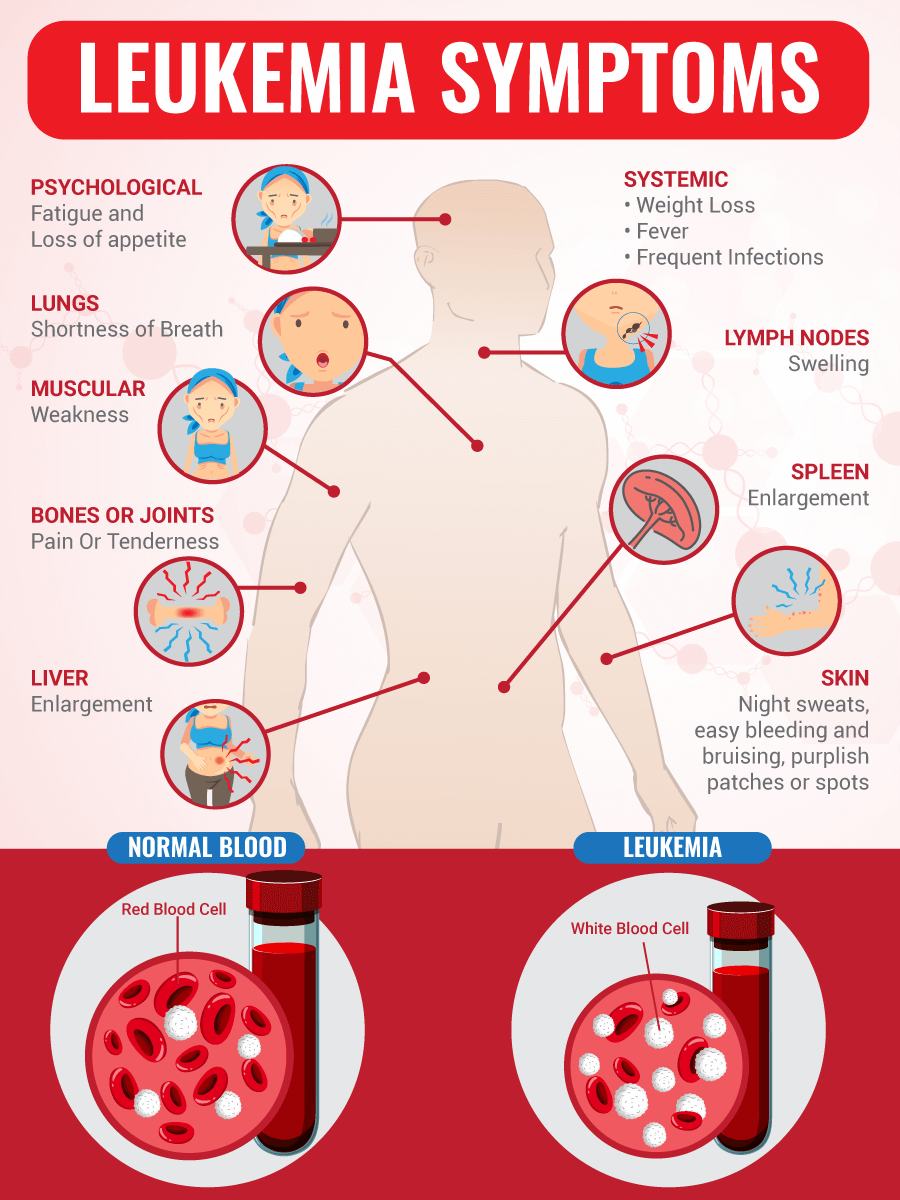
* Some common symptoms of leukemia include:
> Fatigue and weakness: Leukemia can cause a decrease in the number of healthy blood cells, which can lead to fatigue and weakness.
> Infections: People with leukemia are more susceptible to infections due to a weakened immune system.
> Easy bruising and bleeding: Leukemia can interfere with the normal clotting function of the blood, leading to easy bruising and bleeding.
> Pain in bones and joints: Leukemia can cause pain and tenderness in the bones and joints.
> Swollen lymph nodes: Leukemia can cause the lymph nodes to become enlarged.
> Fever and chills: Leukemia can cause fever and chills due to infections or other complications.
> Shortness of breath: Leukemia can cause a decrease in the number of healthy red blood cells, which can lead to shortness of breath.
It's important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, so it's important to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In addition to the above symptoms, the specific symptoms of leukemia can depend on the type of leukemia a person has. Here are some additional symptoms that may be associated with different types of leukemia:
 |
| Understanding Leukemia // Dr. Jockers |
* Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL):
- Enlarged liver or spleen
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpit, or groin
- Headaches and seizures
R E A D : Exploring the Link Between Stress and Major Depressive Disorder: Understanding the Role of Stress Management in Treatment.
* Acute myeloid leukemia (AML):
- Gum bleeding or other bleeding that won't stop
- Skin rash or bumps
- Respiratory symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
* Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL):
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, armpit, or groin
- Recurrent infections
- Night sweats
- Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML):
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Feeling full after eating only a small amount
- Unintended weight loss
The treatment and cure for leukemia depend on the type and stage of the disease, as well as other factors such as the person's age, overall health, and other medical conditions. Some common treatment options for leukemia include:
> Chemotherapy: This is the most common treatment for leukemia, and involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be administered orally, intravenously, or injected into the spinal fluid.
> Radiation therapy: This treatment uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
> Bone marrow transplant: This is a procedure in which a person's diseased bone marrow is replaced with healthy bone marrow from a donor.
> Targeted therapy: This is a newer type of treatment that uses drugs to target specific proteins or genes in cancer cells, while sparing healthy cells.
> Immunotherapy: This treatment uses a person's own immune system to fight cancer cells.
> Clinical trials: There are ongoing clinical trials testing new treatments for leukemia, which may offer promising options for some people.
It's important to note that not all people with leukemia will be cured, but many people are able to achieve long-term remission with proper treatment. In addition to medical treatment, supportive care such as blood transfusions, antibiotics to prevent infections, and other medications may also be necessary to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The treatment and management of leukemia should be tailored to the individual needs of each person, and involve a team of healthcare professionals including oncologists, hematologists, and other specialists.
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, and is characterized by the abnormal growth and proliferation of white blood cells. The exact causes of leukemia are not fully understood, but there are several risk factors that have been identified. Symptoms of leukemia can include fatigue, infections, easy bruising and bleeding, pain in bones and joints, swollen lymph nodes, fever and chills, and shortness of breath. Treatment options for leukemia include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, bone marrow transplant, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and clinical trials. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many people with leukemia are able to achieve long-term remission and live healthy, productive lives. It's important for people at higher risk of developing leukemia to undergo regular check-ups and screenings, and to speak with a doctor if they are experiencing any symptoms or concerns.


No comments:
Post a Comment