Goodbye to Dizziness: Understanding and Treating Ménière's Disease
 |
| The Silent Agony: Unveiling the Mystery of Ménière's Diseas, Healthnews // Lybrate |
Discover the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for Ménière's Disease - Your Ultimate Guide
R E A D : Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: Understanding a Rare Genetic Disorder and its Dental Manifestations
WHAT'S THAT Ménière's disease?
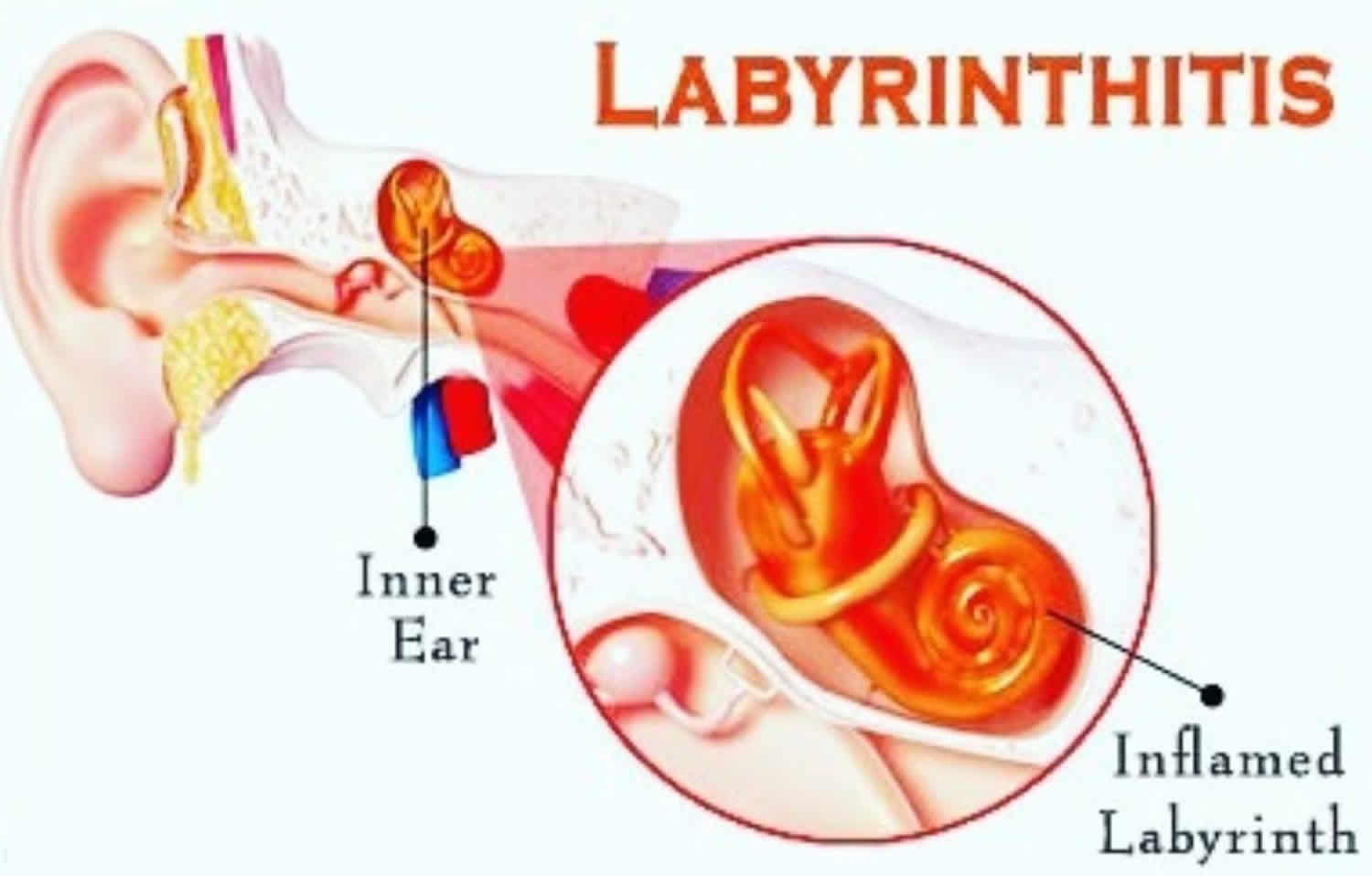
Ménière's disease is a disorder of the inner ear that can cause vertigo (a spinning sensation), hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear. The symptoms of Ménière's disease are caused by an excess buildup of fluid in the inner ear, which can affect the balance and hearing functions of the ear.
Ménière's disease can occur at any age, but it is more commonly diagnosed in people between the ages of 40 and 60. The cause of the disease is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
There is no cure for Ménière's disease, but symptoms can be managed through a combination of medications, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary. It is important to see a healthcare provider if you are experiencing symptoms of Ménière's disease, as prompt treatment can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
What the causes
The exact cause of Ménière's disease is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of factors, including:
- Abnormal fluid buildup: Ménière's disease is thought to be caused by an accumulation of fluid in the inner ear, which can affect the ear's balance and hearing functions.
- Genetics: There may be a genetic component to Ménière's disease, as it often runs in families.
- Autoimmune disorders: Some research suggests that Ménière's disease may be associated with autoimmune disorders, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues.
- Allergies: Allergies or hypersensitivity to certain foods or environmental factors can trigger symptoms of Ménière's disease in some people.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as viral or bacterial infections, may be associated with Ménière's disease in some cases.
- Head trauma: Head injuries or trauma can sometimes trigger symptoms of Ménière's disease.
- Other health conditions: Certain underlying health conditions, such as thyroid disorders, may increase the risk of developing Ménière's disease.
It is important to note that while these factors may increase the risk of developing Ménière's disease, not all individuals with these risk factors will develop the condition, and some individuals without any risk factors may still develop the disease.
 |
| The Silent Agony: Unveiling the Mystery of Ménière's Diseas, Healthnews // Lybrate |
R E A D : Stiff Person Syndrome: Unlocking the Secrets of Autoimmune Muscle Rigidity
What the symptoms
The symptoms of Ménière's disease can vary from person to person, but typically involve episodes of:
- Vertigo: This is a sensation of spinning or dizziness that can be very intense and debilitating. It can last for minutes to hours and may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Hearing loss: Ménière's disease can cause hearing loss, which may be temporary or permanent. The hearing loss often affects low-frequency sounds first and can progress over time.
- Tinnitus: This is a ringing, hissing, or roaring sound in the ears that is often present during or after a vertigo episode.
- Feeling of fullness in the ear: Many people with Ménière's disease report a feeling of pressure or fullness in the affected ear.
Other symptoms that may occur during an episode of Ménière's disease include headache, sweating, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety. In some cases, individuals may experience symptoms of Ménière's disease in only one ear, while in others, both ears may be affected.
Method of treatment
The treatment of Ménière's disease typically involves a combination of medications, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications. The specific treatment plan will depend on the individual's symptoms and the severity of their condition. Some common treatment methods include:
Medications: Medications such as diuretics, antihistamines, and anti-nausea drugs may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of Ménière's disease.
Dietary changes: Some people find that reducing their salt intake and avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and certain foods can help alleviate symptoms of Ménière's disease.
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy: This is a type of physical therapy that can help improve balance and reduce dizziness.
Stress management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms of Ménière's disease, so stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or relaxation exercises may be helpful.
Surgery: In severe cases of Ménière's disease, surgery may be recommended. The two most common surgical options are endolymphatic sac decompression and vestibular nerve section
Important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan for Ménière's disease, as the effectiveness of treatment can vary depending on the individual's specific symptoms and needs.
Ménière's disease is a disorder of the inner ear that can cause vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear. While the exact cause of the disease is not fully understood, it is believed to be related to a combination of factors such as abnormal fluid buildup, genetics, autoimmune disorders, allergies, infections, head trauma, and other health conditions.
Although there is no cure for Ménière's disease, symptoms can be managed through a combination of medications, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications. It is important to see a healthcare provider if you are experiencing symptoms of Ménière's disease, as prompt treatment can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. With proper management, most people with Ménière's disease are able to lead normal, productive lives.
R E A D :
- The Clutter Conundrum: Breaking Free from Hoarding Disorder
- Understanding Labyrinthitis and its Effects on Your Balance and Hearing
- Unlocked Thyroid Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- The Link Between Oral Health Disease and Overall Well-being: Prevention and Treatment Strategies